Get In Touch
Contact Kelly McNamara for information on products, services or locations.
Recent Posts
- Stamping in an EV World Virtual Conference
- Altair Enlighten Award Webinar Series
- Panel Discussion with Material Sciences Corp and Other 2019 Altair Enlighten Award Winners
- MSC SMART STEEL® FEATURED IN STAMPING JOURNAL
- MATERIAL SCIENCES CORPORATION RINGS THE NASDAQ OPENING BELL
Recent Comments
Archives
- May 2021
- March 2021
- May 2020
- February 2020
- September 2019
- August 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- February 2019
- December 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- April 2018
- October 2017
- September 2017
- December 2016
- October 2016
- April 2016
- January 2016
- November 2015
- September 2015
- August 2014
- June 2014
- March 2014
- July 2013
- August 2012
Categories
- Automotive
- Burr Ridge
- Canton
- Careers Testimonials
- Elk Grove Village
- Locations
- News
- Product Testimonials
- Products
- Services
- Turin, Italy
- Uncategorized
- Walbridge
Meta
Top 10 Best Metal Processing Techniques for Efficient Manufacturing
In the realm of manufacturing, metal processing stands as a cornerstone of production efficiency and product quality. As industries continually evolve, the need for innovative techniques in metal processing has become increasingly imperative. The ability to manipulate and transform metals not only influences the performance of the final products but also impacts the sustainability and cost-effectiveness of manufacturing processes.
This article explores the top ten metal processing techniques that have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in contemporary manufacturing. From advanced machining and welding methods to cutting-edge additive manufacturing technologies, these techniques provide manufacturers with the tools necessary to optimize their operations. By adopting these strategies, businesses can enhance their productivity, reduce waste, and ultimately gain a competitive edge in the market.
As we delve into these essential processes, we will examine their unique advantages and applications, helping manufacturers to identify the best practices that align with their production goals. Embracing the right metal processing techniques is paramount for achieving operational excellence in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.

Overview of Metal Processing Techniques in Manufacturing
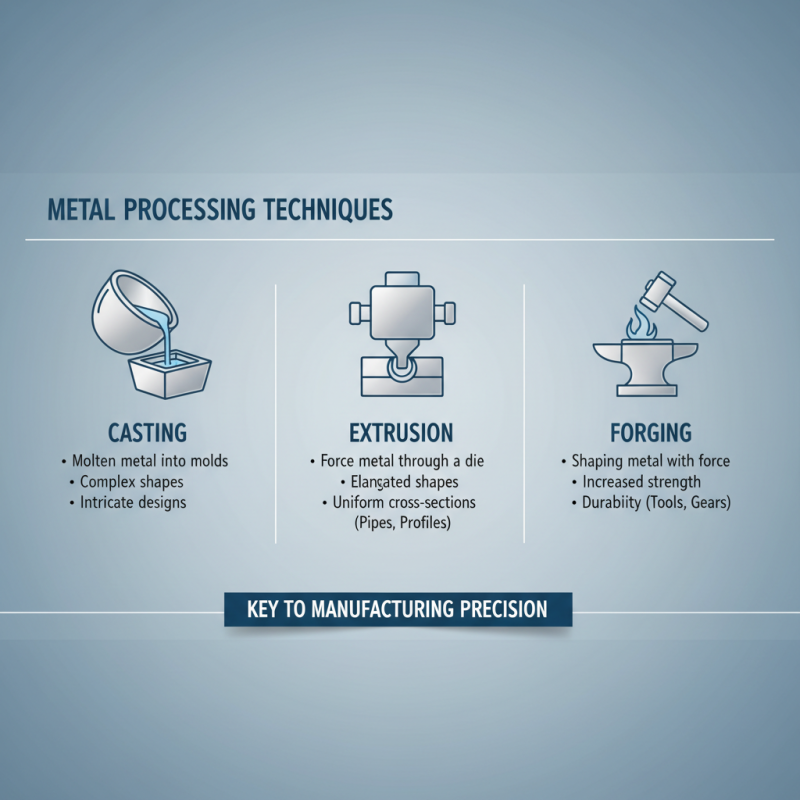
Metal processing techniques play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, enabling the transformation of raw metals into functional and precise components. Among the various methods, processes such as casting, extrusion, and forging stand out for their efficiency and effectiveness. Casting allows for complex shapes to be formed by pouring molten metal into molds, making it ideal for producing components with intricate designs. On the other hand, extrusion involves forcing metal through a die to create elongated shapes with uniform cross-sections, which is particularly useful for manufacturing parts like pipes and profiles.
Another key technique is machining, where material is removed from a workpiece to achieve desired dimensions and surface finishes. Techniques such as turning and milling are widely used to produce high-precision components. Additionally, processes like welding and sheet metal forming contribute to the assembly and shaping of metal parts, ensuring structural integrity and versatility in design. Each of these techniques has its own advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the manufacturing process, highlighting the importance of tailoring metal processing methods to enhance productivity and quality in manufacturing operations.
Importance of Efficiency in Metal Processing
Efficiency in metal processing plays a crucial role in determining the overall success of manufacturing operations. As industries strive to meet increased demand and adhere to stringent quality standards, optimizing metal processing techniques becomes essential. Efficient manufacturing processes not only reduce waste and lower production costs but also enhance productivity and improve product quality. By streamlining operations, manufacturers can respond swiftly to market changes and customer needs, maintaining a competitive edge.
Incorporating efficient techniques into metal processing can lead to significant time savings, allowing for faster turnaround times and improved workflow. Methods such as laser cutting, precision machining, and additive manufacturing are increasingly being adopted due to their ability to execute complex designs while minimizing material usage. Moreover, advancements in technology, such as automation and real-time monitoring, contribute to more consistent production outcomes. By prioritizing efficiency, manufacturers can achieve better resource utilization, ensure timely deliveries, and ultimately boost profitability, solidifying their position in an ever-evolving market landscape.
Top 10 Best Metal Processing Techniques for Efficient Manufacturing - Importance of Efficiency in Metal Processing
| Technique | Description | Efficiency Benefits | Industry Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Computer-controlled cutting and shaping of metals. | High precision, reduced waste. | Aerospace, automotive, manufacturing. |
| Metal Injection Molding | Combines molding and injection techniques to create complex shapes. | Complex parts with minimal processing time. | Medical devices, consumer goods. |
| Hydraulic Pressing | Uses hydraulic force to shape metals. | High force application, good for thick materials. | Automotive, appliance manufacturing. |
| Laser Cutting | Uses focused laser beams to cut through metal. | High precision cuts, minimal thermal distortion. | Sign making, automotive parts. |
| Water Jet Cutting | Utilizes high-pressure water jets to cut materials. | No heat affected zones, versatile materials. | Architecture, aerospace, metalwork. |
| Additive Manufacturing | Builds 3D objects layer by layer from metal powders. | Custom designs, reduced material use. | Aerospace, medical implants. |
| Forging | Deforming metals with compressive forces. | Improves strength and toughness. | Aerospace, military applications. |
| Bending | Changing the shape of metal sheets. | Fast processing, various angles and shapes. | Construction, auto parts. |
| Welding | Joining metals by melting and fusing. | Strong bonds, versatile applications. | Manufacturing, construction. |
Detailed Analysis of the Top 10 Metal Processing Techniques
Metal processing techniques play a critical role in modern manufacturing, impacting efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and output quality. Among the top techniques, precision machining stands out, with a projected market growth of 5.3% annually, as revealed in recent market analysis reports. This method utilizes advanced tools and CNC machines to remove material with high accuracy, facilitating the production of complex components for aerospace and automotive industries. Precision machining not only improves product quality but also reduces waste, underscoring its significance in enhancing manufacturing efficiencies.
Another notable technique is additive manufacturing, which has gained significant traction, particularly in industries requiring intricate designs. According to a report from a leading industry research firm, the additive manufacturing market is expected to reach $35.4 billion by 2025, driven by its ability to create lightweight and durable metal parts without the constraints of traditional fabrication methods. This technique allows manufacturers to optimize their designs and customize components quickly, leading to faster turnaround times and reduced material costs. By integrating additive manufacturing within their processes, companies can achieve greater flexibility and innovation in product development, making it a key player in efficient metal processing.
Top 10 Best Metal Processing Techniques for Efficient Manufacturing
Comparison of Techniques Based on Material and Application
When evaluating metal processing techniques, it is essential to consider the specific materials and applications being utilized. Different techniques offer distinct advantages depending on the properties of the metals involved. For instance, welding and brazing are commonly employed for joining metals, with their effectiveness varying significantly between ferrous and non-ferrous materials. Ferrous metals, such as steel, often benefit from traditional welding methods due to their higher melting points and structural integrity, whereas non-ferrous metals like aluminum require specialized techniques such as TIG welding to prevent oxidation and achieve a strong bond.
Moreover, techniques like laser cutting and waterjet cutting present unique benefits based on the application. Laser cutting is known for its precision and is particularly advantageous for intricate designs and thick materials, making it ideal for detailed fabrication work. Conversely, waterjet cutting offers versatility since it can effectively process a wider range of materials, including those sensitive to high heat, without altering their structural properties. Each technique’s suitability is determined by factors such as material thickness, the desired finish, and operational efficiency, highlighting the importance of selecting the right method tailored to specific manufacturing needs.
Future Trends in Metal Processing Techniques for Enhanced Productivity
The landscape of metal processing techniques is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for higher efficiency in manufacturing. One of the most significant trends is the incorporation of automation and robotics into metal processing workflows. Automated systems not only enhance precision but also significantly reduce processing time and labor costs, allowing manufacturers to focus on more complex tasks that require human expertise. Furthermore, smart technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) sensors are being integrated into machinery to gather real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Another key trend is the adoption of advanced materials and processes, such as additive manufacturing and hybrid machining. These innovative techniques allow for the production of complex geometries that were previously impossible with traditional methods. Additive manufacturing, in particular, offers the potential for significant reductions in material waste and energy consumption, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices. As the industry continues to embrace these advanced techniques, the focus on sustainability and eco-efficient processes will be paramount, ensuring that metal processing not only meets current demands but also aligns with future environmental standards.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 Metal Materials: Innovations Shaping the Future of Manufacturing
-

How to Improve Efficiency in Metal Manufacturing Processes in 2025
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Coil Coating for Your Architectural Projects
-

How to Choose the Right Material for Your Science Project Successfully
-

How to Choose the Right Steel Metal for Your Project
-

Ultimate Guide to Coil Coating Tips for Superior Finish and Durability
