Get In Touch
Contact Kelly McNamara for information on products, services or locations.
Recent Posts
- Stamping in an EV World Virtual Conference
- Altair Enlighten Award Webinar Series
- Panel Discussion with Material Sciences Corp and Other 2019 Altair Enlighten Award Winners
- MSC SMART STEEL® FEATURED IN STAMPING JOURNAL
- MATERIAL SCIENCES CORPORATION RINGS THE NASDAQ OPENING BELL
Recent Comments
Archives
- May 2021
- March 2021
- May 2020
- February 2020
- September 2019
- August 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- February 2019
- December 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- April 2018
- October 2017
- September 2017
- December 2016
- October 2016
- April 2016
- January 2016
- November 2015
- September 2015
- August 2014
- June 2014
- March 2014
- July 2013
- August 2012
Categories
- Automotive
- Burr Ridge
- Canton
- Careers Testimonials
- Elk Grove Village
- Locations
- News
- Product Testimonials
- Products
- Services
- Turin, Italy
- Uncategorized
- Walbridge
Meta
What is the Impact of Steel Industries on Global Economy and Environment?
The steel industries play a pivotal role in the global economy. In 2022, the global crude steel production reached approximately 1.87 billion tons, according to the World Steel Association. This figure highlights the massive output of the sector. The industry is crucial for infrastructure, automotive, and construction sectors. Steel is essential for modern development.
However, the environmental impact of steel production raises concerns. Steel industries contribute to around 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Many plants rely on coal as a primary energy source. This reliance challenges sustainability goals. The process not only consumes vast resources but also affects air quality and biodiversity.
A shift towards greener alternatives is necessary. Innovations like electric arc furnaces can reduce emissions significantly. Though progress exists, many companies are still behind. They must reflect on their practices. The balance between economic benefits and environmental responsibilities is delicate. Sustainable practices are essential for the future of the steel industries.
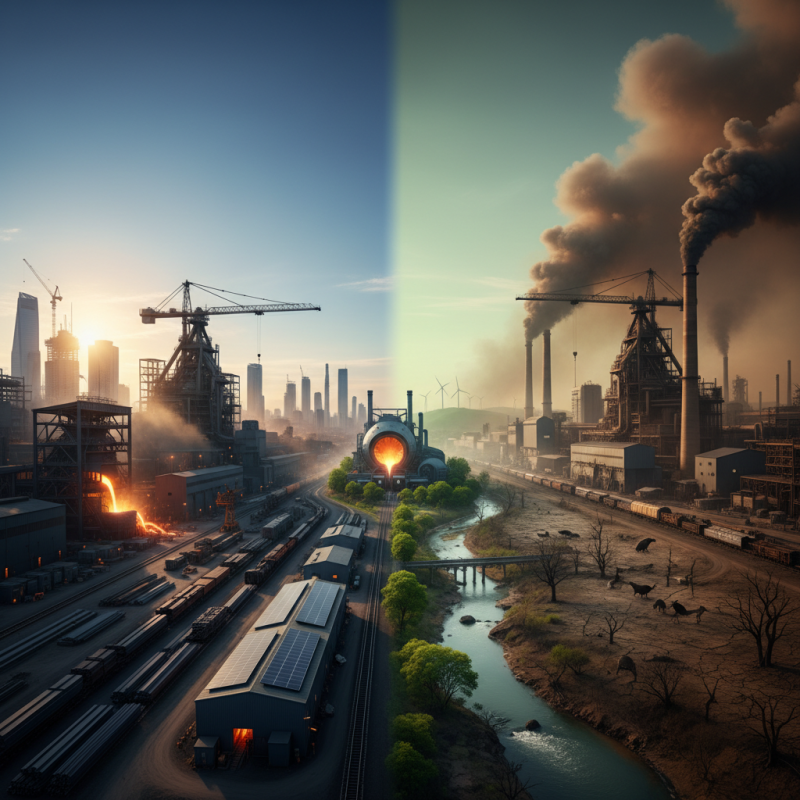

The Role of Steel Industries in the Global Economy

The steel industry plays a crucial role in the global economy. It supports infrastructure projects and manufacturing. Steel is essential for building skyscrapers, bridges, and cars. These products drive economic growth. Moreover, steel is a key component of renewable energy projects, like wind turbines.
However, the steel industry's environmental impact is significant. Manufacturing steel generates a large amount of CO2 emissions. This contributes to climate change and air pollution. Many countries are now looking for greener steel production methods. The challenge lies in balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
Tips: Consider the carbon footprint of steel production. Supporting innovations in this sector can lead to a cleaner future. Always advocate for sustainable practices in construction. Small changes can make a big difference.
Impact of Steel Production on Employment and Trade
The steel industry plays a crucial role in global employment and trade. In 2021, the sector provided approximately 1.5 million direct jobs in the United States alone. This number is significant, but challenges remain. Many workers face job insecurity due to automation and globalization. The transition to greener technologies also puts traditional jobs at risk.
Trade in steel products is substantial. In 2022, global steel production reached around 1.9 billion tons. Countries export steel to meet demand, generating billions in revenue. However, this growth has not been even. Developing nations often struggle with trade barriers, limiting their market access. It sparks a reflection: while the steel industry boosts employment, its benefits are unequally distributed.
Environmental costs are another concern. Steel production emits a significant amount of CO2. In 2020, it was responsible for around 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Balancing economic growth and environmental protection is difficult. Many companies are adopting cleaner practices, but the pace is slow. Job growth can’t overshadow the need for sustainable strategies.
The Impact of Steel Industries on Global Economy and Environment
This chart illustrates the impact of steel production on employment and trade within the global economy. The data represents different countries and their corresponding employment figures and trade values associated with the steel industry.
Environmental Challenges Faced by the Steel Industry
The steel industry is a major contributor to global economic growth. However, it faces significant environmental challenges. Steel production emits a large amount of carbon dioxide. This contributes to climate change and air pollution. The extraction of raw materials also disturbs ecosystems. Forests are destroyed, and wildlife habitats are lost.
Water pollution is another critical issue. Heavy metals and toxins often leach into local waterways during production. This severely impacts aquatic life and community health. In many regions, communities near steel plants face health risks. Harmful emissions affect air quality, leading to respiratory problems.
Recycling steel is an important step toward sustainability. It reduces the need for raw materials and lowers emissions. Yet, only a fraction of steel is recycled globally. The industry must find ways to innovate and improve practices. Focus on cleaner technologies is necessary. A shift in mindset is needed from rapid production to responsible management. There is much room for improvement.
Technological Innovations in Steel Production and Their Economic Effects
Technological innovations in steel production are transforming the industry. Automation and advanced robotics are increasing efficiency. Factories now use machine learning for quality control. This shift minimizes errors and waste. These processes can lead to lower production costs. However, the initial investment in technology is high.
On the environmental side, newer methods reduce emissions significantly. Electric arc furnaces, for instance, can use recycled steel. This conserves resources and reduces the carbon footprint. Yet, not all steel mills have adopted these technologies. Many still rely on outdated methods that harm the environment.
The economic impact is notable. Countries that embrace innovation see growth in the steel sector. Job opportunities increase, but skill gaps remain. Workers need training to adapt to new technologies. The pace of innovation may outstrip workforce readiness. This is a challenge that requires careful consideration.
What is the Impact of Steel Industries on Global Economy and Environment?
| Country | Steel Production (Million Tonnes) | Contribution to GDP (%) | CO2 Emissions (Million Tonnes) | Technological Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 1063 | 7.2 | 1005 | Electric Arc Furnace |
| India | 100 | 8.9 | 225 | Blast Furnace & DRI |
| USA | 88 | 1.7 | 140 | Recycling Steel |
| Japan | 83 | 1.5 | 99 | Float Glass Technology |
| Germany | 42 | 2.4 | 55 | Hydrogen Reduction |
Sustainability Practices and the Future of the Steel Industry
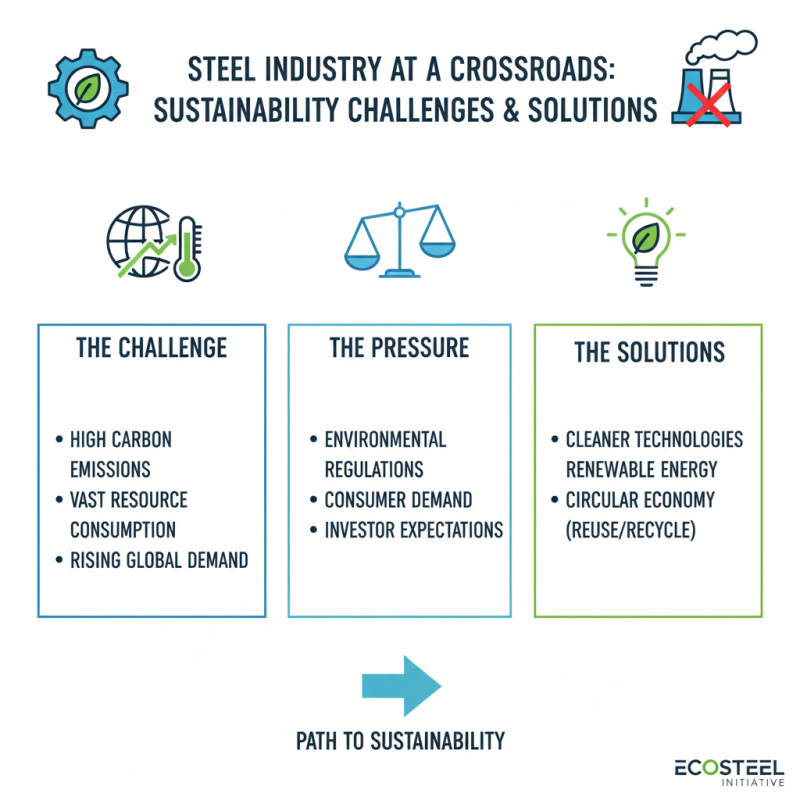
The steel industry is at a crossroads regarding sustainability. Its operations produce significant carbon emissions and consume vast resources. As global demand for steel rises, the pressure to adopt sustainable practices intensifies. Many companies are now investing in cleaner technologies to reduce their environmental footprint.
Innovative methods are emerging, such as using renewable energy sources for steel production. Some facilities are exploring electric arc furnaces instead of traditional blast furnaces. These changes could lead to more efficient processes and lower emissions. However, challenges remain. Many plants still rely heavily on fossil fuels, and transitioning can be costly.
Furthermore, recycling old steel is another crucial aspect. It requires less energy and reduces waste. Yet, the global steel recycling rate varies. Some regions lag in these practices, prompting concerns about material waste. The future of steel hinges on a collective commitment to sustainability. Despite progress, much work lies ahead. The industry must rethink its priorities and practices to balance economic growth and environmental responsibility.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Steel Corporations You Should Know About in 2023
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Steel Material for Your Project
-

2025 Top 5 Metal Materials: Innovations Shaping the Future of Manufacturing
-

How to Succeed in the Metal Industry Tips for Growth and Efficiency
-

10 Smart Steel Tips for Sustainable Construction and Design Innovations
-

Ultimate Guide to Coil Coating Tips for Superior Finish and Durability
